Welcome back to the Diamonds Hatton Garden blog where we bring you the latest in our bespoke diamond jewellery designs, share our knowledge of the diamond industry and discuss our passion for diamonds. Have you ever heard of the 4 cs? When looking to buy a piece of diamond jewellery be it a diamond engagement ring or even a loose diamond, it is common, when researching, to come across the term “The 4cs”. In today’s blog we explore what “The 4 Cs” of diamonds are and what they mean as a buyer.
Buying a piece of diamond jewellery can be a difficult and daunting experience for a newcomer. It may be hard to understand the value of a certain diamond suggested for a piece of jewellery and it can also be difficult to understand why certain diamonds are more expensive and valued higher than others. We have put together a useful guide where you will be able to understand what “The 4 Cs” of diamonds are and what to look for when purchasing a loose diamond.
What are the 4 Cs in the Diamond Industry?
The 4 Cs are the grading methods used within the diamond industry to assess (or grade) the quality of a diamond. Established by the GIA (The Gemological Institute of America) the 4 Cs are an abbreviation of (Carat Weight, Cut, Colour, Clarity) and refer to the four main characteristics of a diamond that affect both its desirability and price. Each diamond certified by the GIA (the most respected gemological association in the World) is accompanied by a certificate that details the 4 Cs of the diamond as well as more information.
Carat Weight
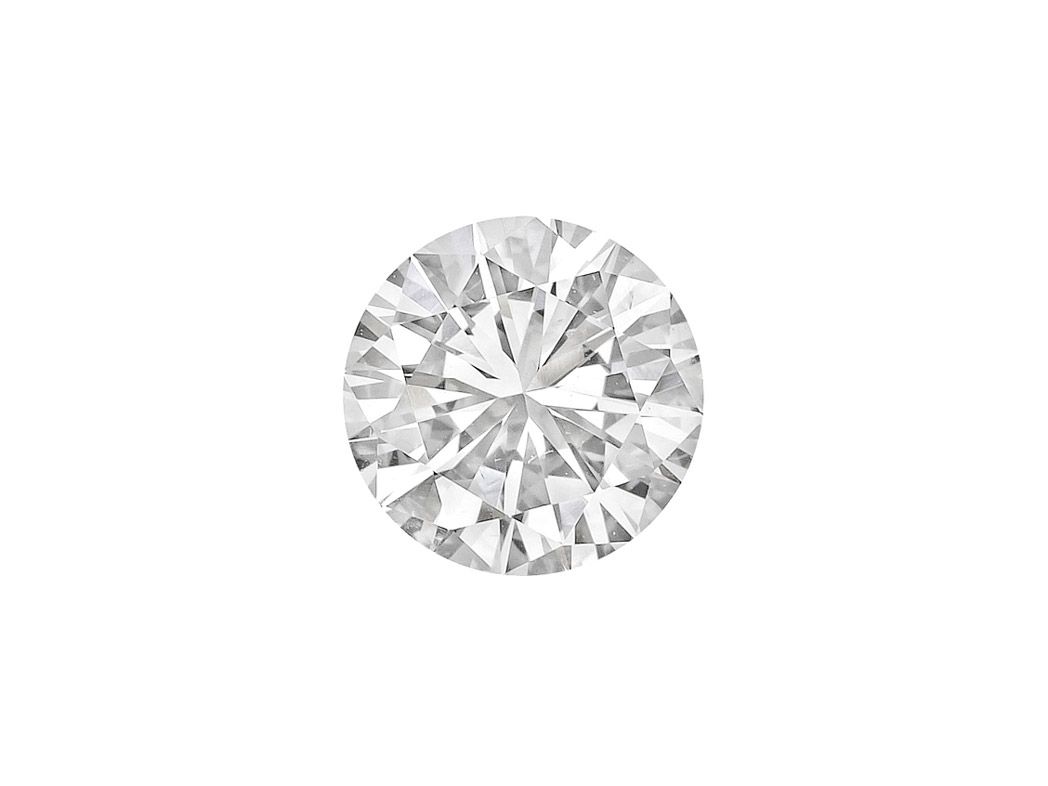
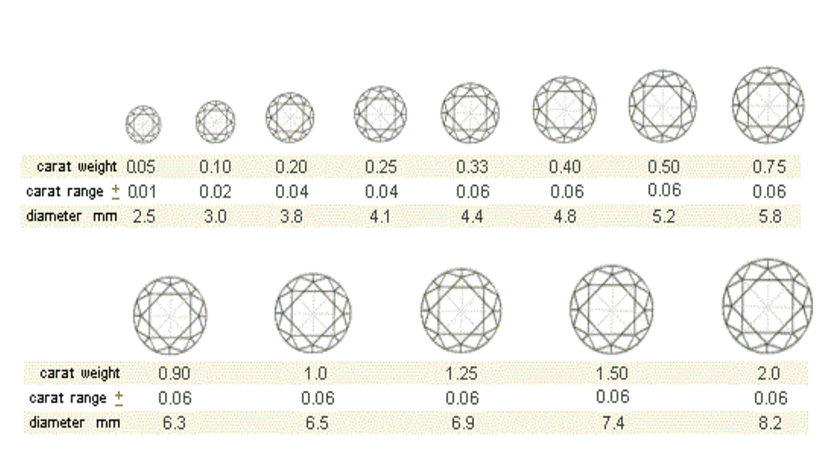
Diamonds are sold by a unit of measurement that is know as a carat (shown as ct.), whilst it is commonly seen as a unit of weight it can also be understood as a measurement of size as well. The word carat itself is derived from the term carob which was the original size used by diamond traders to measure diamonds many centuries ago, Nowadays, a single carat is equivalent to 0.2 grams.
The carat weight of a diamond is, specifically, one of the 4 main grades used by the GIA when assessing diamonds and other factors, such as colour, cut and clarity) also have an impact on the overall price of a diamond. For example, two diamonds of equal carat weight can have differing prices based on the other factors.
Indeed, as the carat weight of the diamond increases so does the price of the stone itself. This is because the larger the diamond the more rare it is. For example, less than one in 1 million mined diamonds are above a 1 carat finished diamond reflecting their rarity. What’s more, as the size increases so does the price on a price per carat scale.
Colour of a Diamond
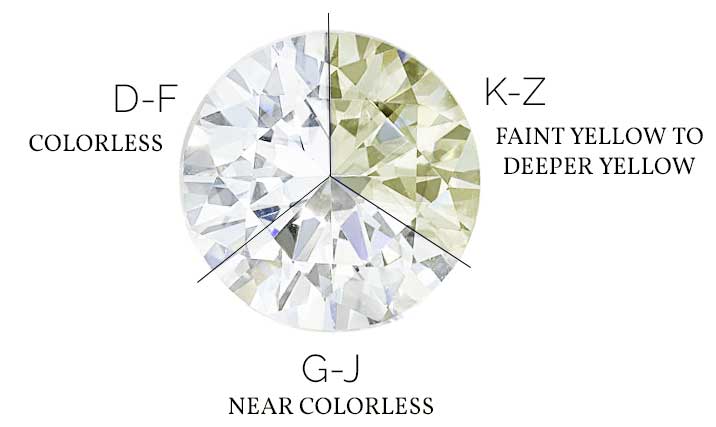
The colour of a diamond is part of the 4Cs and, literally, refers to the colour of the diamond. Much like the carat weight of a diamond, a diamond’s colour has an impact on its price and value. White diamond are graded from D-Z and the higher the diamond’s colour is on the scale the “cleaner” and more pure the colour is. Gemologists use a master set of images and loose diamonds in order to grade their colour. Each diamond is graded relative to the master set in order to establish where it lies within the colour scale. D,E and F coloured diamonds are the most in demand as they are the rarest naturally occurring colours within the gemstones. When grading the colour of a diamond they are usually placed crown down (not the pointy top) as by assessing a diamond in this position it is easier to establish the body colour and reduce both the fire and brightness. It is always advisable when setting D,E and F coloured diamonds to use a neutral coloured setting such as silver or platinum as the colours of yellow and rose gold can reflect within the diamond thus reducing the natural beauty of such wonderfully coloured stones. Much like carat weight, the further you move up the colour chart of diamonds (from Z-D) the higher the price of the stone due to its rarity.
Cut of a Diamond
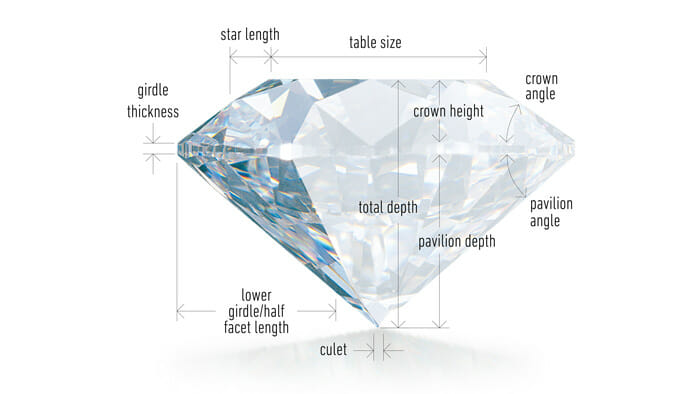
The cut of a diamond refers to the proportion, symmetry and polish of a cut diamond and is commonly confused with the shape of a diamond. What we would consider to be the beauty of a diamond is normally related to the cut of the stone as it is here that the beauty of the craftsman is shown. The cut of a diamond causes three very distinct effects to occur on the stone and effects the appearance; Brilliance, fire and scintillation. The brilliance of a diamond refers to the brightness that is refracted inside the cut stone from the reflections and inside of the polished diamond. Fire refers to how the like dissipates within the stones and the flashes of colour that can occur. Finally, the scintillation of a diamond is the sparkle that occurs from the light source. Why is the cut of a diamond important? The cut of a diamond is extremely important as it gives, in essence, live to the stone. A diamond may have immaculate colour, clarity and carat, but if it only reflects little light then it will look dull and lifeless. However, a diamond with a great cut will sparkle and look alive.
Clarity of a Diamond
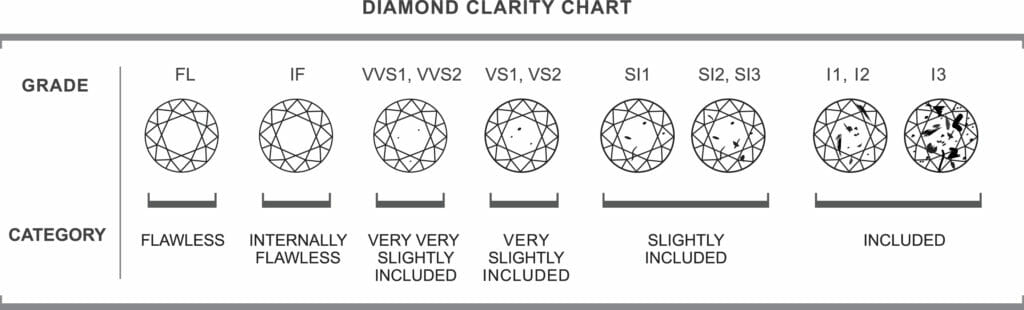
The clarity of a diamond refers to how clear a diamond appears internally and should not be confused with the colour of a diamond. Formed under intense pressure and deep in the earth, diamonds have been subject an immense process in their creation. Nearly all diamonds contain blemishes (small imperfections) within the inside and outside of the stone. Imperfection on the inside of the stone are known as inclusions and those on the surface are known as blemishes. Clarity essentially refers to the level in which these inclusions or blemishes are present within a polished stone, Diamonds that have a higher number have less brilliance because the imperfections affect how the light passes through the stone.
Indeed, where the inclusion internally sits within a diamond affects how it is seen. When a diamond is being cut, diamond cutters cut the stone in a way that minimises how visible the inclusions are. The clarity of a diamond is graded on a 11 point scale and is measured by taking into the account the amount, size, colour, reflectivity, and position of every flaw visible under 10x magnification.
Are you looking to purchase a diamond or a piece of elegant diamond jewellery? As jewellers in Hatton Garden our expert teams have, for over 40 years, helped clients across the world. Contact our teams to arrange a personal appointment via info@diamondshg.co.uk or on +44 (0) 7951 060238.

